- India Location w.r.t. World: Of the world India comes in Northern Hemisphere or North-East part.
- The southernmost point of the country is the Pygmalion Point, or Indira Point is located at 6° 45′ N latitude.
- North-south extent from Indira Col in Kashmir to Kanyakumari is 3,214 km.
East West Extent of India:
- East-west width from the Rann of Kutch to Arunachal Pradesh is 2,933 km.
- Following table will help you remember the Geographical Extent:
| East-West Extent | 68° 7′ East to 97° 25′ East longitude |
| South-North Extent of mainland India (Including POK) | 8° 4′ North to 37° 6′ North latitude |
| South-North Extent of India (Including POK and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands) | 6° 45′ North to 37° 6′ North latitude |
Total Geographic Area of India:
- With an area of 32,87,263 km , India is the seventh largest country in the world.
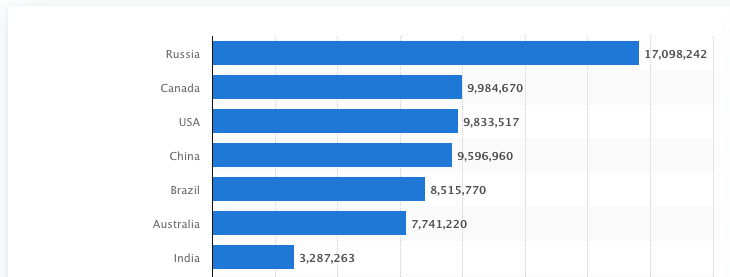
- India accounts for about 2.4 % of the total surface area of the world.
- The Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of the country dividing it into two latitudinal halves.
- The area to the north of Tropic of Cancer is near twice the area which lies to the south of it.
- South of 22° north latitude, the country tapers off over 800 km into the Indian Ocean as a peninsula.
- East-West time difference is nearly 2 hrs. (A dif-ference of 1° longitude will make a difference of 4 minutes in time. ~30 x 4 = ~120 minutes or ~2 hours).
India’s frontiers
- India’s longest border is with Bangladesh and shortest border is with Afghanistan (PoK touches Afghanistan).
- Land Border: 15106.7 Km running through 17 States.
- Coastline: India has a coastline of 7516.6 Km (6100 km of mainland coastline + coastline of 1197 Indian islands) touching 13 States and Union Territories (UTs).
- Frontline states: States which touches the boundary with other countries, or International borders or coastline.
- Exception to frontline states: Telangana, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattis- garh, Jharkhand, Delhi and Haryana.
| Neighbouring country | Length of the common border (in km) | No. of states with common borders | Names of Indian states having common borders |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bangladesh | 4096 | 5 | West Bengal, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram |
| China | 3488 | 5 | Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh |
| Pakistan | 3323 | 4 | Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, Gujarat |
| Nepal | 1751 | 5 | Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, Sikkim |
| Myanmar | 1643 | 4 | Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram |
| Bhutan | 699 | 4 | Sikkim, West Bengal, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh |
| Afghanistan | 106 | 1 | Jammu & Kashmir (POK) |
1. India-China Border
- Second largest border after Bangladesh.
- States touches the Boundary with China:
| 01 | Jammu and Kashmir |
| 02 | Himachal Pradesh |
| 03 | Uttarakhand |
| 04 | Sikkim |
| 05 | Arunachal Pradesh |
- The Indo-China border is divided into three sectors:
- the Western Sector
- the Middle Sector
- the Eastern Sector
1. The Western Sector
- Length: 2152 km long border separates Jammu and Kashmir from Sinkiang province of China.
- The frontier between Sinkiang and Pakistan Occupied Kashmir is about 480 km. Long.
- The Western sector Boundary is an outcome of British Policy towards Jammu and Kashmir. Known as Laddakh tibet Agreement.
- Chinese claims that Aksai Chin is just an extension of Tibet with regards to language, religion and culture.
- The Indians, on the other hand claim that the area has been historically administered by the state of Jammu and Kashmir since 1849.
2. The Middle Sector
- Boundary: 625 km. Long
- States touring this border: (i). Himachal Pradesh (ii). Uttarakhand.
- Important rivers near: Spiti and Para Chin and Kalia and Alaknanda.
3. The Eastern Sector
- 1140 km long boundary between India and China runs from Eastern limit of Bhutan to point near Talu Pass at Tri-junction of India, Tibet and Myanmar.
- This is also Called as Mac Mohan line: Why it is so? Because Mac Mohan foreign secretory of British government of Indian negotiated Boundary agreement between Great Britain and Tibet also known as Shimla Accord in 1913-14.
2. India-Nepal Border
- Length: 1752 Kilometer long.
- State touching the boundary: 5 States
| 01 | Uttarakhand |
| 02 | Uttar Pradesh |
| 03 | Bihar |
| 04 | West Bengal |
| 05 | Shimla |
- Major portion runs in the east-west direction almost along foothills of Shiwalik Range.
3. India-Bhutan Border
- Bhutan Shares 587 km long border with India. Bhutan is protection form external invasion.
- Bhutan has friendly relation with India based on 1949 treaty. Under this treaty, India has got the rights to protect Bhutan’s sovereignty and defend its borders.
4. Indo-Pakistan Border

- The Indo-Pakistan boundary is the result of the partition of the country in 1947 under the Rad- cliffe award of which Sir Cyril Radcliffe was the chairman.
- Jammu and Kashmir, Sir Creek are the major disputed regions.
- This boundary has created several disputes from Runs of Kachchh to Jammu and Kashmir.
5. The India-Bangladesh Border
- Longest and nearly 27% of total land border of India.
- 5 Indian States share boundary with Bangladesh.
| 01 | West Bengal |
| 02 | Assam |
| 03 | Meghalaya |
| 04 | Tripura |
| 05 | Mizoram |
- West Bengal has 2,272 Km. long border with Bangladesh.
- This boundary has been determined under the Radcliffe Award which divided the erstwhile province of Bengal into two parts.
6. India-Myanmar Boundary
- Length: 1458 km long.
- This Boundary runs roughly along the watershed between the Brahmaputra and Ayeyarwady.
- It passes through thickly forested regions, with Mizo Hills, Manipur and Nagaland on the Indian side and Chin Hills, Naga Hills and Kachin state on the Myanmar side.
7. India-Sri Lanka Boundary
- India and Sri Lanka are separated from each other by a narrow and shallow sea called Palk Strait.
- Dhanushkodi on the Tamil Nadu coast in India is only 32 km away from Talaimanar in Jaffna peninsula in Sri Lanka. These two points are joined by a group of islets forming Rama Setu (Adam’s Bridge).
Credit Sources/References
More Topics on Geography:
| Rock System | Indo-Gangatic Brahmaputra plain |
| Himalayan Ranges | Peninsular Plateau |
| Coastline of India | Indian Islands |
| Drainage system of India | Indian Monsoon |
| Indian Climate | Natural Vegetation of India |





